In Silico Exploration of Orthosiphon stamineus Compounds as Potential Angiotensin Receptor Blockers for Hypertension Therapy
Abstract
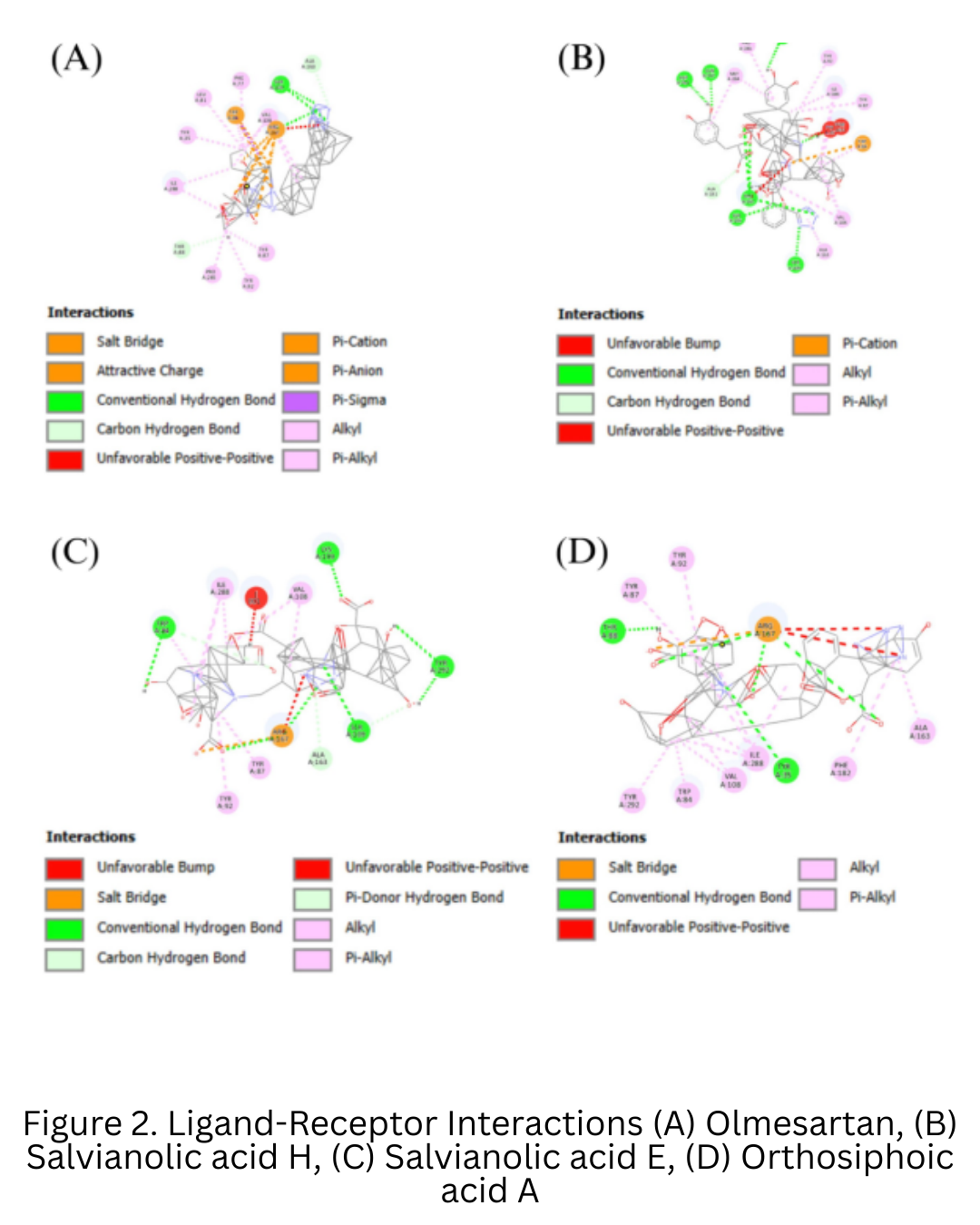
Orthosiphon stamineus has demonstrated antihypertensive potential, but the specific bioactive compounds involved remain unclear. This study aimed to evaluate selected phytochemicals from O. stamineus as angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) targeting protein 4ZUD using in-silico methods. Molecular docking was conducted to assess binding affinity, while ADMET analysis evaluated pharmacokinetics and toxicity. Salvianolic acid E showed the strongest binding affinity with a rerank score of −134.02 kcal/mol, surpassing olmesartan (−124.52 kcal/mol). Key interactions were observed with amino acid residues Arg167, Tyr92, and Asp281. ADMET predictions revealed that Salvianolic acid E has good aqueous solubility, moderate intestinal absorption (HIA 45.99%), and low membrane permeability (Caco-2 < 0.4). It does not inhibit major cytochrome P450 isoenzymes and is predicted to be non-hepatotoxic, suggesting favorable safety and metabolic profiles. These findings highlight Salvianolic acid E as a promising phytochemical candidate for antihypertensive drug development.
Full text article
References
Agamah, E., Osei, D. N. A., & Sekyere, A. A. (2020). Pharmacoinformatics-based approach for potential HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors from African natural products as anti-hyperlipidemic agents. Heliyon, 6(2), e03486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03486
Bagas, A. F., Soesanti, F., & Murwani, R. (2021). Perbandingan model machine learning dan deep learning untuk klasifikasi penyakit jantung. Jurnal RESTI (Rekayasa Sistem dan Teknologi Informasi), 5(6), 1048–1056. https://doi.org/10.29207/resti.v5i6.3685
Bitencourt-Ferreira, G., & de Azevedo, W. F. (2019). Development of a machine-learning model to predict Gibbs free energy of binding for protein-ligand complexes. Biophysical Chemistry, 245, 25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2018.12.002
Chen, H. (2015). A novel ensemble learning approach for imbalanced data learning. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 53, 303–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2014.11.010
Konsensus Penatalaksanaan Hipertensi. (2019). Konsensus penatalaksanaan hipertensi 2019. Perhimpunan Dokter Hipertensi Indonesia.
Lestari, N. D., Wibowo, A. S., & Setiadi, R. (2023). Perbandingan metode klasifikasi machine learning untuk deteksi penyakit jantung. Jurnal Ilmu Komputer dan Informatika, 7(1), 40–46. https://doi.org/10.30865/jifo.v7i1.4661
PERKI. (2015). Pedoman tatalaksana hipertensi di Indonesia. Perhimpunan Dokter Spesialis Kardiovaskular Indonesia.
Prasetiyo, A. B., Anshory, A., & Suryani, D. (2019). Evaluasi performa algoritma klasifikasi untuk prediksi penyakit jantung. Jurnal Teknik Informatika, 12(1), 15–22. https://doi.org/10.20961/jti.v12i1.35654
Sulistyowaty, A., Wahyuningrum, T., & Maulida, A. (2023). Penerapan algoritma klasifikasi untuk mendeteksi risiko hipertensi pada pasien rawat jalan. Jurnal Sains dan Informatika, 9(2), 67–73. https://doi.org/10.32520/jsi.v9i2.2760
Thomsen, M., & Christensen, M. (2006). Bayesian networks in pharmacoepidemiology: A literature review. Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, 15(8), 619–627. https://doi.org/10.1002/pds.1247
WHO. (2021). Hypertension. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Gou, L., Yang, L., Wang, H., & Wang, H. (2020). Research on heart disease prediction based on random forest and ensemble learning. Healthcare Technology Letters, 7(4), 128–132. https://doi.org/10.1049/htl.2019.0022
Yanith, A. R., Ginting, F. D., & Siregar, A. I. (2021). Penerapan algoritma decision tree untuk prediksi penyakit jantung. Jurnal Teknik Informatika dan Sistem Informasi, 7(2), 87–92. https://doi.org/10.31933/josis.v7i2.664
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Copyright @2017. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial used, distribution and reproduction in any medium