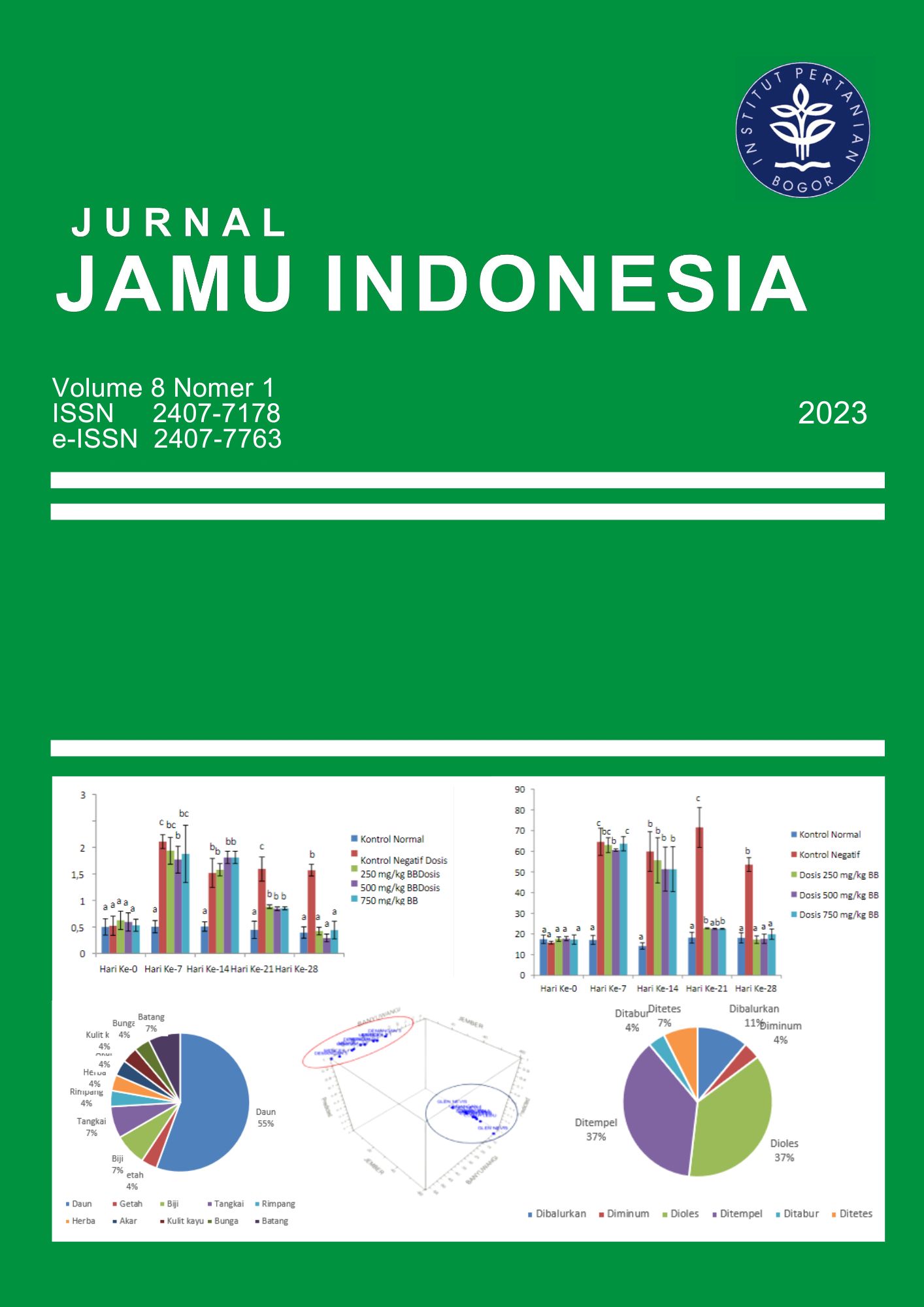
Review: Extraction of Temulawak Rhizome (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb.) and Activity As Antibacterial
Abstract
Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza) is one of Indonesia’s native plants belonging to Zingiberaceae family. The plant has been extensively used for treatment of various diseases such as inflammation and digestive tract swelling, gallstones, liver, dyspepsia, and antispasmodic. The rhizome becomes the plant’s part that is used the most. The rhizome contains a compound that could work as an antibacterial. An extract of the rhizome may be obtained through extraction process, some extractions that would be used in this research review is soxhletation, maceration, and ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE). As various extraction methods both involving simple and complex ones were found, it was shown that the result of extract content are therefore varied, which was also affecting the level of resulted antibacterial effectiveness. This article was carried out to analyze the most suitable extraction method of Curcuma’s rhizome that results the highest effectiveness of antibacterial activity. The method used in this article review was a literature review on the literatures published during the period of 2012 to 2022. The highest average yield was shown on maceration method which respectively was followed by soxhletation whereas the lowest yield was resulted by UAE method
Full text article
References
Ajusha S, Gangaprasad A. 2014. Phytochemical and Antibacterial Analysis of Two Important Curcuma species, Curcuma aromatica Salisb. and Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb. (Zingiberaceae). Journal of Pharmacognosy and Photochemistry. 3(3): 50-53.
Alexander DKN. 2015. Ekstrak Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorriza Roxb) terhadap resisten staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Majority. 4(8): 177-184.
Amelinda E, Widarta IWR, Darmayanti LPT. 2018. Pengaruh Waktu Maserasi Terhadap Aktivitas Antioksidan Ekstrak Rimpang Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorriza Roxb.). Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Pangan (ITEPA). 7(4): 165–174.
Anggoro D, Rezki RS, Siswarni, MZ. 2015. Ekstraksi Multi Tahap Kurkumin dari Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorriza Roxb.) Menggunakan Pelarut Etanol. Jurnal Teknik Kimia USU. 4(2). pp. 40-43.
Atun S, Aznam N, Arianingrum R, Senam S, Naila BIA, Lestari A, Purnamaningsih NA. 2020. Characterization of Curcuminoid from Curcuma xanthorrhiza and Its Activity Test as Antioxidant and Antibacterial. Molekul. 15(2): 79-87.
Ayu HR, Suryono S, Suseno JE. 2020. Rancang Bangun Sistem Ultrasound Assisted Extraction (UAE) dengan Otomasi Pengaturan Suhu dan Volume Pelarut. Indonesian Journal of Applied Physics. 10 (1): 56-63
Azemi N, Basar N, Toemen S. 2020. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE) of Phytochemicals with Response Surface Methodology (RSM) in Curcuma Xanthorrhiza. International Journal of Advance Science and Technology. 29(10):.3431-3450
Azimah D, Yuswanto, Wahyono, Santosa D, Setyowati PE. 2015. Efek Imunomodulator Dari Kombinasi Ekstrak Etanol Herba Sambiloto (Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Nees) Dan Rimpang Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb.) Terhadap Proliferasi Sel Limfosit Mencit Balb/C Secara In Vitro. Traditional Medicine Journal. 20(2): 157-168.
Azmir, J. et al. 2013. Techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials. Journal Of Food Engineering. 117: 426-436.
Buanasari, Febrianto Y, Cholifah, Chakim A. 2019. Potensi Metode Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction (UAE) Dalam Mengekstrak Senyawa Aktif Dari Bahan Alam. Jurnal Farmasi & Sains Indonesia Vol. 2 (1) : 106-111
Cahyono B, Ariani J, Failasufa H, Suzery M, Susanti S, Hadiyanto H. 2019. Extraction Of Homologous Compounds Of Curcuminoid Isolated From Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb.) Plant. Rasayan J. Chem. 12 (1): 7-13
Chairunnisa S, Ni Made W, Lutfi S. 2019. Pengaruh Suhu dan Waktu Maserasi terhadap Karakteristik Ekstrak Daun Bidara (Ziziphus mauritiana L.) sebagai Sumber Saponin. Jurnal Rekayasa dan Manajemen Agroindustri. 7(4): 551-560.
Kumar K, Srivastav S, Sharanagat VS. 2021. Ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) of bioactive compounds from fruit and vegetable processing by-products: A review. ELSEVIER. 70: 1-11.
Magani AK, Tallei TE, Kolondam BJ. 2020. Uji Antibakteri Nanopartikel Kitosan terhadap Pertumbuhan Bakteri Staphylococcus aureus dan Escherichia coli. Jurnal Bios Logos. 10(1): 7-12
Maleta HS, Indrawati R, Limantara L, Brotosudarmo THP. 2018. Ragam Metode Ekstraksi Karotenoid dari Sumber Tumbuhan dalam Dekade Terakhir (Telaah Literatur). Jurnal Rekayasa Kimia & Lingkungan. 13(1): 40–50.
Menon S, Satria A. 2017. Mengkaji Aktivitas Antibakteri Nasturtium officinale dan Ekstrak Etanol Pilea melastomoides terhadap Escherichia coli. Farmaka. 15(1): 63-69
Mustikaturrokhmah D, Risanti ED. 2020. Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Etanol 70% Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb.) Terhadap Staphylococcus epidermidis dan Salmonella thyposa In Vitro. Herb-Medicine Journal. 3(3): 47-51.
Novianti D, Kartika T. 2019. Fractionation of Bioactive Materials Temulawak Rhizome (Curcuma xanthorrhiza) on Fungal Candida albicans In Search of Phytopharmaca. Journal of Physics: 1-6.
Nurhadi B, Saputra RA, Setiawati TA, Husein SN, Faressi FR, Utari CD, Nukri N, Kayaputri IL, Setiasih IS. 2019. Comparison of Curcuma domestica and Curcuma xanthorrhiza oleoresins extracted using maceration, Soxhlet, and ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE). International Conference on Food and Bio-Industry. 1(1): 1-10.
Purnamaningsih NA, Kalor H, Atun S. 2017. Uji Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Temulawak (Curcuma Xanthorrhiza) Terhadap Bakteri Escherichia Coli ATCC 11229 dan Staphylococcus Aureus ATCC 25923. Jurnal Penelitian Saintek. 22(2): 140–147.
Puspitasari AD, Proyogo LS. 2017. Perbandingan Metode Ekstraksi Maserasi Dan Sokletasi Terhadap Kadar Fenolik Total Ekstrak Etanol Daun Kersen (Muntingia calabura). Jurnal Ilmiah Cendekia Eksakta. 2(1): 1-8.
Sa’adah H, Nurhasnawati H. 2015. Perbandingan Pelarut Etanol Dan Air Pada Pembuatan Ekstrak Umbi Bawang Tiwai (Eleutherine americana Merr) Menggunakan Metode Maserasi. Jurnal Ilmiah Manuntung. 1(2): 149-153.
Savitri NH, Indiastuti DN, Wahyunitasari MR. 2019. Inhibitory Activity Of Allium Sativum L. Extract Against Streptococcus Pyogenes and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Journal of Vocational Health Studies. 3(2): 72-77.
Septiani, Dewi EN, Wijayanti I. 2017. Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Lamun (Cymodocea Rotundata) Terhadap Bakteri Staphylococcus aureus Dan Escherichia coli. IJFST. 13(1).
Sumiati. 2019. Kertas Indikator Asam Basa Dari Ekstrak Etanol Rimpang Tanaman Temulawak (Curcuma Xanthorrhiza Roxb.). Integrated Lab Journal. 7(2): 119-131.
Siswarni MZ, Yusrina IP, Rizka RP. 2017. Ekstraksi Kuersetin dari Kulit Terong Belanda (Solanum betaceum Cav.) menggunakan Pelarut Etanol dengan metode Maserasi dan Sokletasi. Jurnal Teknik Kimia USU. 6(1): 36–42.
Susilowati T, Kawiji, Ariviani S. 2014. Kapasitas antioksidan dan kadar kurkuminoid pada ekstrak rimpang temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb) menggunakan pelarut air dengan variasi proporsi pelarut dan metode pemanasan. Biofarmasi, 12(4): 83–9.
Syamsudin RAMR, Perdana F, Mutiaz FC. Galuh V, Rina APA, Cahyani ND, Aprilya S, Yanti R, Khendri F. 2019. Tanaman Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb) Sebagai Obat Tradisional. Jurnal Ilmiah Farmako Bahari. 10(1): 51-65.
Wahyuni WT, Herdiyanto, Rafi M. 2017. Metode Ekstraksi dan Pemisahan Optimum Untuk Isolasi Xantorizol dari Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza). Jurnal Jamu Indonesia. 2(2): 43–50.
Warmasari NWM, Ernawati DK, Indrayani AW, Dewi NWS, Jawi IM. 2020. Antibacterial Activity From Temulawak Extract (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb) On Growth Inhibition of Staphylococcus epidermidis In Vitro. Jurnal Epidemiologi Kesehatan Komunitas. 5(1): 1–7.
Wewengkang DS, Rotinsulu H. 2021. FITOFARMAKA. Klaten: Penerbit Lakeisha.
Widyastuti I, Luthfah HZ, Hartono YI. Islamadina R. Can AT. Rohman A. 2020. Antioxidant Activity of Temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb.) and its Classification with Chemometrics. Indonesian Journal of Chemometrics and Pharmaceutical Analysis. 2(1): 29.
Yurleni. 2018. Penggunaan Beberapa Metode Ekstraksi Pada Rimpang Curcuma Untuk Memperoleh Komponen Aktif Secara Kualitatif. Biospecies. 11(1): 1–9.
Zahrah H, Mustika A, Debora K. 2018. Aktivitas Antibakteri dan Perubahan Morfologi dari Propionibacterium Acnes Setelah Pemberian Ekstrak Curcuma Xanthorrhiza. Jurnal Biosains Pascasarjana. 20(3): 160–169.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Copyright @2017. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial used, distribution and reproduction in any medium