Anti-inflammatory Activity of Ipomoea batatas Leaves Ethanolic Extract Tablet with Variation of Polyvinylpyrrolidone and Amylum Binders
Abstract
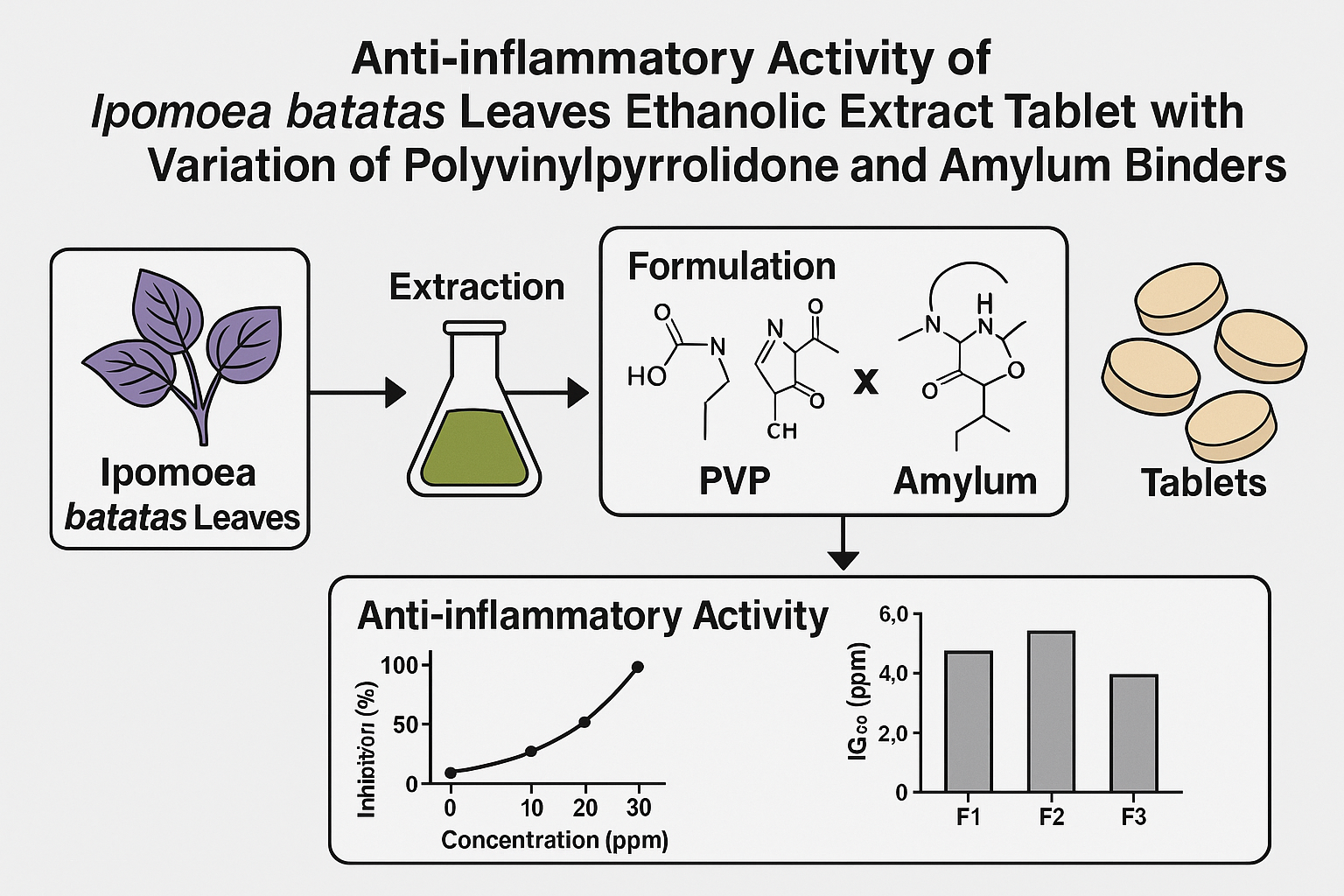
Purple sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) leaves are traditionally used as an anti-inflammatory remedy. This study investigated the anti-inflammatory activity of purple sweet potato leaf ethanolic extract and its formulation into tablet dosage forms with varying concentrations of polyvinylpyrrolidone and amylum as binders. The extract was obtained through maceration using 96% ethanol and tested for anti-inflammatory activity using the bovine serum albumin denaturation method. The extract showed strong anti-inflammatory activity with an IC₅₀ value of 62.628 ppm compared to sodium diclofenac with an IC₅₀ of 57.326 ppm. The extract was then formulated into tablets with binder ratios of 1:0, 0:1, 1:1, 2:3, and 1:4 (polyvinylpyrrolidone: amylum) using wet granulation. Evaluation of physical properties indicated that the 1:1 binder ratio produced tablets that met quality requirements, including hardness, friability, and disintegration time. These results suggest that I. batatas leaf extract has potent anti-inflammatory properties and is suitable for development into a tablet formulation with appropriate binder ratios.
Full text article
References
Depkes RI. (1979). Farmakope Indonesia (Edisi III). Jakarta: Direktorat Jenderal Pengawasan Obat dan Makanan.
Depkes RI. (2014). Farmakope Indonesia (Edisi V). Jakarta: Direktorat Jenderal Pengawasan Obat dan Makanan.
Depkes RI. (2020). Farmakope Indonesia (Edisi VI). Jakarta: Direktorat Jenderal Pengawasan Obat dan Makanan.
Farida, Y., Rahmat, D., & Amanda, A. W. (2018). Uji aktivitas antiinflamasi nanopartikel ekstrak etanol rimpang temulawak (Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb.) dengan metode penghambatan denaturasi protein. Jurnal Ilmu Kefarmasian Indonesia, 16(2), 225–230.
Kurakula, M., & Rao, G. S. N. K. (2020). Pharmaceutical assessment of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP): As excipient from conventional to controlled delivery systems with a spotlight on COVID-19 inhibition. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 60, 102046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102046
Kurnia, D., Prisdayanti, N., Marliani, L., & Nurochman, Z. (2019). Aktivitas antiinflamasi ekstrak mikroalga laut Chlorella vulgaris dengan metode stabilitas sel darah merah manusia. Jurnal Kartika Kimia, 2(November), 57–62.
Lachman, L., Lieberman, H. A., & Kanig, J. L. (1994). Teori dan praktek farmasi industri. Jakarta: Universitas Indonesia Press.
Lidyawati, L., Dita, S. F., & Agustiany, C. M. (2021). Uji skrining fitokimia ekstrak etanol daun ubi jalar ungu (Ipomoea batatas L.). Journal of Pharmaceutical and Health Research, 2(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.47065/jharma.v2i1.778
Minarti, R., Ruga, R., & Marliana, E. (2021). Aktivitas antiinflamasi ekstrak metanol daun pare hutan (Momordica balsamina Linn.) dalam menghambat denaturasi protein. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Kimia 2021, 103–107.
Okta, O. P., & Laili, R. T. N. (2023). Antimicrobial activity of temu blenyeh (Curcuma purpurascens Blume) ethanol extract against Streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans. Ad-Dawaa’ Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 6(1), 93–101. https://doi.org/10.24252/djps.v6i1.37703
Pramiastuti, O., & Murti, F. K. (2022). Fitokimia dan aktivitas antioksidan ekstrak temu blenyeh (Curcuma purpurascensBlume). Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan, 15(1), 12–22. https://doi.org/10.48144/jiks.v15i1.627
Ramadhani, N., & Sumiwi, S. A. (2016). Aktivitas antiinflamasi berbagai tanaman diduga berasal dari flavonoid. Farmaka, 14(2), 111–123.
Sari, R. P., Pambudi, D. B., Rahmatullah, S., & Ningrum, W. A. (2021). Pengaruh perbedaan pati singkong (Manihot esculenta Crantz) pragelatinasi dan PVP sebagai bahan pengikat terhadap sifat fisik tablet kalsium laktat (Skripsi Sarjana, Universitas Muhammadiyah Semarang).
Setyowati, W. A. E., Ariani, S. R. D., Ashadi, Mulyani, B., & Rahmawati, C. P. (2014). Skrining Fitokimia dan Identifikasi Komponen Utama Ekstrak Metanol Kulit Durian (Durio zibethinus Murr.) Varietas Petruk. Seminar Nasional Kimia Dan Pendidikan Kimia VI, 271–280. https://adoc.tips/skrining-fitokimia-dan-identifikasi-komponen-utama-ekstrak-m.html
Siregar, C., & Wikarsa, S. (2008). Teknologi farmasi sediaan tablet dasar-dasar praktis (J. Manurung, Ed.). Jakarta: EGC.
Voight, R. (1995). Buku pelajaran teknologi farmasi. Yogyakarta: Gadjah Mada University Press.
Waluyo, E., Pambudi, D. B., & Slamet, S. (2021). Uji aktivitas antiinflamasi ekstrak etanol, fraksi metanol dan fraksi n-heksan daun ubi jalar ungu (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) dengan metode stabilitas membran sel darah merah secara in vitro (Laporan penelitian, Universitas Jenderal Soedirman).
Widianti, Z. (2017). Efek antiinflamasi ekstrak etanol daun zaitun (Olea europaea L.) pada edema telapak kaki tikus galur Sprague-Dawley jantan yang diinduksi karagenan (Skripsi Sarjana, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta).
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Copyright @2017. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial used, distribution and reproduction in any medium